Macruby Support in any Cocoa Application
May 06, 2009Yesterday I published a post about Cocoa Prototyping with Webview and today I found out about Macruby thanks to @sarnesjo. Already looking for ways of prototyping in Cocoa it’s hard to not find Macruby very interesting.
Macruby turns out to be a very powerful tool for prototyping (as well as writing entire applications in) as it fits perfectly fine in a normal Objective-C code base. What I wanted was something like this:
class SimpleController
attr_accessor :label
attr_accessor :button
attr_accessor :my_view
def buttonPressed(sender)
label.setStringValue("I am (im)pressed!")
my_view.backgroundColor = NSColor.redColor
end
endWhere the view :my_view is implemented in Objective-C.
Here are the simple steps I used to hook it into a normal Xcode Cocoa project.
First of all, install Macruby which is as easy as downloading the zip-file from the website and run the installer.
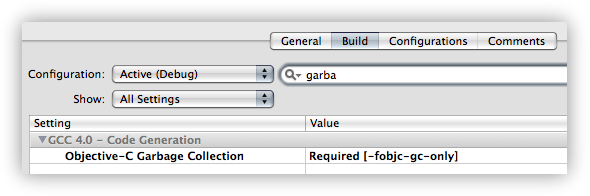
In order to link to the Macruby framework you need to use garbage collection in your project, if you aren’t already you enable it in the project inspector:
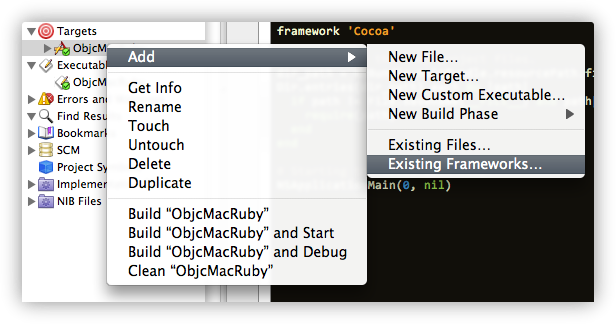
Next you need to make your project link against the Macruby framework:
That’s it for the project settings, let’s hook it up in the code. When you use the built-in project template for a Macruby project a small Ruby file called rb_main.rb is created for you. Since I’m using a generic Cocoa application template I needed to create this file and simply copied the file into my new project (its code below). It loads all Ruby files in your bundle and starts the Cocoa main loop.
# Loading the Cocoa framework. If you need to load more frameworks, you can
# do that here too.
framework 'Cocoa'
# Loading all the Ruby project files.
dir_path = NSBundle.mainBundle.resourcePath.fileSystemRepresentation
Dir.entries(dir_path).each do |path|
if path != File.basename(__FILE__) and path[-3..-1] == '.rb'
require(path)
end
end
# Starting the Cocoa main loop.
NSApplicationMain(0, nil)To start the actual Ruby interpreter the file main.m needs to be modified. Since the Ruby code now starts the Cocoa main loop we no longer need to do that in main. Main.m simply becomes:
#import <MacRuby/MacRuby.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
return macruby_main("rb_main.rb", argc, argv);
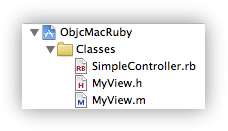
}With these changes you can now start writing code in either Ruby or Objective-C within the same project. Here are the files I ended up with in my very small example.
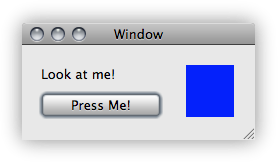
The final application simply shows a small window with a button:
Make sure to watch the great introductionary screencast then download the example project and get started tinkering.
If you find this as cool and useful as I did, let me hear about it!
Edit: Be sure to read Laurents comment below for an alternative way of loading your Ruby files into your application.